Cold storage is essential in industries where maintaining low temperatures is crucial for preserving the quality and safety of products. From the food industry to pharmaceuticals and chemical manufacturing, cold storage applications are vital for extending the shelf life of products, preventing spoilage, and ensuring regulatory compliance. Understanding the key aspects of cold storage can help you optimize your operations and maintain the integrity of your goods.
1. Types of Cold Storage Facilities
There are various types of cold storage facilities, each designed to meet specific temperature and storage requirements. Selecting the right type of facility is crucial to ensure that your products are stored in optimal conditions.
Refrigerated Warehouses:
Refrigerated warehouses are large-scale facilities designed to store perishable goods at temperatures typically ranging from 0°C to 10°C (32°F to 50°F). These facilities are commonly used for fruits, vegetables, dairy products, and other items that require cooling but not freezing.

Fruit and Vegetable Cold Rooms
Freezer Storage:
Freezer storage facilities maintain temperatures below 0°C (32°F), often reaching as low as -18°C (-0.4°F) or lower. These facilities are essential for storing frozen foods, ice cream, and certain pharmaceuticals that require long-term freezing to preserve their quality.
Blast Freezers:
Blast freezers are specialized cold storage units that rapidly freeze products to very low temperatures, typically between -30°C and -40°C (-22°F to -40°F). This quick freezing process helps prevent the formation of large ice crystals, preserving the texture and quality of food products.
2. Importance of Temperature Control
Maintaining precise temperature control is critical in cold storage applications. Even slight variations in temperature can lead to product spoilage, compromising safety and quality. Here's why temperature control is so important:

Quick-Freezing Cold Storage
Product Integrity:
Temperature fluctuations can cause products to degrade, spoil, or lose their efficacy. For example, certain pharmaceuticals must be kept within a specific temperature range to remain effective, while food products can spoil quickly if not stored at the correct temperature.
Energy Efficiency:
Proper temperature management also impacts energy consumption. Efficient temperature control systems can reduce energy costs by preventing overcooling or overheating, which can strain refrigeration equipment and increase utility bills.
Regulatory Compliance:
Many industries are subject to strict regulations regarding the storage of temperature-sensitive products. Ensuring accurate temperature control helps businesses comply with industry standards and avoid costly fines or product recalls.
3. Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Insulation plays a key role in maintaining the desired temperature within cold storage facilities. High-quality insulation materials help reduce heat transfer, ensuring that the cold air remains inside the storage area while minimizing energy consumption.
XPS Foam Board Insulation:
Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) foam board is a popular insulation material for cold storage facilities. It offers excellent thermal resistance and moisture resistance, making it ideal for use in walls, floors, and roofs of cold storage units.
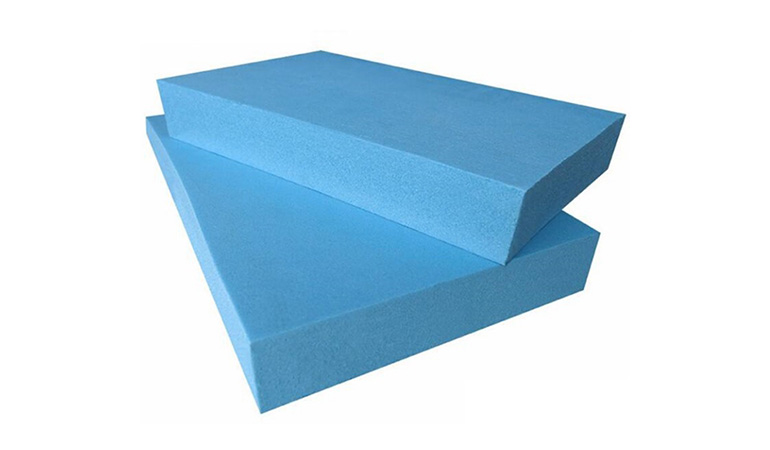

XPS Foam Board
Polyurethane Foam:
Polyurethane foam is another common insulation material used in cold storage applications. It provides high thermal resistance and can be sprayed or applied in panels to create a seamless barrier that minimizes heat gain.
Energy-Efficient Doors and Seals:
In addition to insulation, using energy-efficient doors and seals is crucial for preventing air leakage in cold storage facilities. Automatic doors with tight seals help maintain consistent temperatures and reduce energy loss when accessing stored products.
4. Monitoring and Maintenance
Regular monitoring and maintenance of cold storage facilities are essential to ensure their efficient operation and prevent potential issues that could compromise product quality.
Temperature Monitoring Systems:
Implementing advanced temperature monitoring systems allows for real-time tracking of storage conditions. These systems can alert operators to any deviations from the desired temperature range, enabling quick corrective actions to prevent product spoilage.
Regular Equipment Maintenance:
Routine maintenance of refrigeration equipment, including compressors, condensers, and evaporators, is crucial to prevent breakdowns and ensure optimal performance. Regularly checking and replacing worn-out components can extend the lifespan of the equipment and reduce the risk of costly repairs.

Cold Storage for Vegetables and Fruits
Preventative Measures:
Implementing preventative measures, such as regular inspections and cleaning, helps maintain the efficiency of cold storage facilities. This includes checking for air leaks, inspecting insulation integrity, and ensuring that door seals are functioning properly.
5. Cold Storage Safety Considerations
Safety is a paramount concern in cold storage applications, particularly when dealing with extreme temperatures and hazardous materials. Implementing safety measures can protect both workers and products.
Proper Training:
Ensuring that workers are properly trained in handling cold storage equipment and materials is essential for preventing accidents and injuries. Training should cover safe operation procedures, emergency protocols, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE).
Emergency Procedures:
Establishing clear emergency procedures for cold storage facilities is vital. This includes having a plan in place for power outages, equipment failures, or temperature fluctuations that could put stored products at risk.
Fire Safety:
Although cold storage facilities are designed to maintain low temperatures, fire safety remains a concern. Installing fire suppression systems and ensuring proper ventilation can help mitigate the risk of fires in these environments.
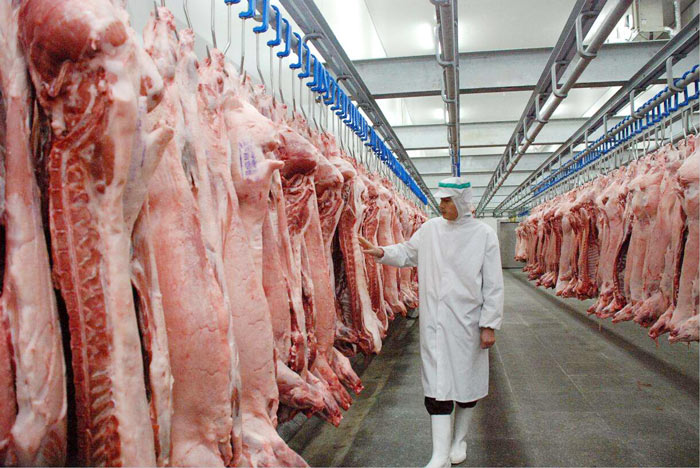

Meat Cold Storage Solutions
Frequently Asked Questions About Cold Storage Applications
Q: What is the difference between cold storage and freezer storage?
A: Cold storage refers to maintaining temperatures above freezing, typically between 0°C and 10°C (32°F to 50°F), while freezer storage involves temperatures below freezing, often as low as -18°C (-0.4°F) or lower. Cold storage is used for products that require cooling, while freezer storage is for products that need to be kept frozen.
Q: How can I improve the energy efficiency of my cold storage facility?
A: Improving insulation, using energy-efficient doors and seals, regularly maintaining refrigeration equipment, and implementing advanced temperature monitoring systems can significantly enhance the energy efficiency of your cold storage facility.
Q: What are the most common challenges in cold storage management?
A: Common challenges in cold storage management include maintaining consistent temperatures, managing energy costs, ensuring regulatory compliance, and preventing equipment breakdowns. Regular monitoring, maintenance, and training can help address these challenges effectively.
Cold storage applications are critical for preserving the quality and safety of temperature-sensitive products. By understanding the different types of cold storage, the importance of temperature control, and the key considerations for insulation, energy efficiency, and safety, you can optimize your cold storage operations and ensure the longevity of your products.
Kendall offers a vast choice of cold rooms, refrigeration equipment and accessories. Whatever your application, whatever your budget, and whatever size and shape for your needs.